Dear All.........., How is going.........? all is well......
As a part of knowledge sharing, Today I want to explain you
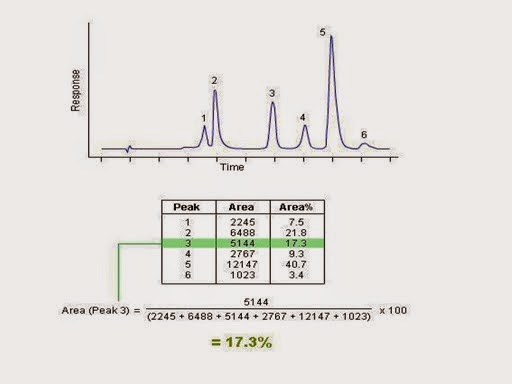
The %Area Normalization procedure reports the area of each peak in the chromatogram as a
percentage of the total area of all peaks. %Area does not require any standard and does not depend upon the amount of sample injected within the limits of the detector.
If all components respond equally in the detector and are eluted, then %Area provides a
suitable approximation of the relative amounts of components.
This is very simple and easy to do.
But......,
There are certain Limitations to % Area normilization method.
(-) This method is applicable only when the responce of all peaks are equal.
(-) This method is applicable only when the all components of sample are eluted in single run.
(-) This method is applicable only when the all peaks are free from interferences and no carry-over.
2) Linearity curve method:
A Linearity curve is a graphical representation of the amount(concentration) versus response(area) for a single analyte (compound) obtained from a series of standard injections.
The curve is usually constructed by injecting an aliquot of the standard solution of known concentration and measuring the peak area obtained. Peak height is sometimes used but only in exceptional circumstances.
Here, C = Intercept represents systematic error
m = Slope represents analytical sensitivity
Check correlation coefficient (R) and it should not be less than 0.999, then inject sample solution.
From sample solution, you will get response(area) which is 'Y'. Calculate amount(concentration) which is 'X' by using regression equation.
This quantitative method can be used where the response of the analyte is considerable low.
3) External Standard Method:
The external standard (ESTD) quantitation procedure is the most common quantification procedure in which both standard and samples are analysed under the same conditions.
Inject standard solution in replicates( No. of injections are based on requirement) and evaluate system suitability (%RSD, Tailing, Plate counts, etc......) and inject sample. Calculate results based on following formula
Amount = (area of sample / avg. area of STD) x ( STD dilutions/ sample dilutions)
In case of Related substances, Relatitive Response Factor(RRF) should be established to the impurities with respect to main analyte.
AND NOW..............
we reached to our main part........
4) Internal Standard Method:
The Internal Standard (ISTD) method eliminates the disadvantages of the External Standard method by adding a known amount of a new component that serves as a normalizing factor.
The way of analysis and caculation is similar to External Standard Method.
External Standard Method : Area of analyte
Internal Standard Method : Ratio of anlyte area and Internal standard area
"The internal standard is added to both standard and unknown samples and ‘compensates’ for losses during sample preparation or variability during the analytical determination."
Internal Standard Method is used ....
a) if there is a routine variation in injection volume( e.g Manual injectors)
b) if there is complex procedure for sample preparation ( large procedure in sample preparation, extraction techniques, etc...)
c) if there is small retention time shifts( RT variation from injection to injection).
Some Care and Considerations should be taken while using Internal Standards.
Care:
* Same quantity of Internal standard should be added to both standard and Sample solutions. Otherwise it may lead to errors.
* Internal Standard concentration should be same in both sample and standard solutions.
* If Large procedure for sample preparation or extraction procedure is used, Internal standard should be added at the first step itself.
Considerations:
* The internal Standard should be similar to analyte chemically and physically.
* The internal Standard should elute near to main analyte and well resolved.
* The internal Standard should not present in Orginal Sample matrix.
* The internal Standard should be unreactive to sample matrix.
* The internal Standard should be availabel in high pure form
* The concentration of Internal standard should be about to half (either in height or response) to the main analyte. (this is to distinguish two peaks instantly in case of RT shifting).
As a part of knowledge sharing, Today I want to explain you
" Use of Internal Standards in HPLC "
Yesterday, While travelling from Hyderabad to Hosur..., One of my beloved research associate asked about "Use of Internal standard in HPLC".
So dear friend(s)....., Come we will jump into one region of knowledge ocean......
We all knows that HPLC can be used for " Identification, product characterization, Purity determination and quantification" purposes.
There are different types of Quantitation methods in HPLC analysis.
Internal Standard Method is one type of Quantitative method used in HPLC & GC analysis.
Types of quantitative analysis using HPLC:
There are mainly 1) Area Normalization method.
2) Linearity Curve method.
3) External Standard method.
4) Internal Standard method.
1) Area Normalization method:
percentage of the total area of all peaks. %Area does not require any standard and does not depend upon the amount of sample injected within the limits of the detector.
If all components respond equally in the detector and are eluted, then %Area provides a
suitable approximation of the relative amounts of components.
This is very simple and easy to do.
But......,
There are certain Limitations to % Area normilization method.
(-) This method is applicable only when the responce of all peaks are equal.
(-) This method is applicable only when the all components of sample are eluted in single run.
(-) This method is applicable only when the all peaks are free from interferences and no carry-over.
2) Linearity curve method:
A Linearity curve is a graphical representation of the amount(concentration) versus response(area) for a single analyte (compound) obtained from a series of standard injections.
The curve is usually constructed by injecting an aliquot of the standard solution of known concentration and measuring the peak area obtained. Peak height is sometimes used but only in exceptional circumstances.
Before injecting sample solution, a series of standard solutions covering target concentration of sample should be injected. Plot a linearity curve using Amount(concentration) versus response(area).
The general regression equation for linearity plot is Y = mX +C
m = Slope represents analytical sensitivity
Check correlation coefficient (R) and it should not be less than 0.999, then inject sample solution.
From sample solution, you will get response(area) which is 'Y'. Calculate amount(concentration) which is 'X' by using regression equation.
This quantitative method can be used where the response of the analyte is considerable low.
3) External Standard Method:
The external standard (ESTD) quantitation procedure is the most common quantification procedure in which both standard and samples are analysed under the same conditions.
Inject standard solution in replicates( No. of injections are based on requirement) and evaluate system suitability (%RSD, Tailing, Plate counts, etc......) and inject sample. Calculate results based on following formula
Amount = (area of sample / avg. area of STD) x ( STD dilutions/ sample dilutions)
In case of Related substances, Relatitive Response Factor(RRF) should be established to the impurities with respect to main analyte.
AND NOW..............
we reached to our main part........
4) Internal Standard Method:
The Internal Standard (ISTD) method eliminates the disadvantages of the External Standard method by adding a known amount of a new component that serves as a normalizing factor.
The way of analysis and caculation is similar to External Standard Method.
External Standard Method : Area of analyte
Internal Standard Method : Ratio of anlyte area and Internal standard area
"The internal standard is added to both standard and unknown samples and ‘compensates’ for losses during sample preparation or variability during the analytical determination."
Internal Standard Method is used ....
a) if there is a routine variation in injection volume( e.g Manual injectors)
b) if there is complex procedure for sample preparation ( large procedure in sample preparation, extraction techniques, etc...)
c) if there is small retention time shifts( RT variation from injection to injection).
Some Care and Considerations should be taken while using Internal Standards.
Care:
* Same quantity of Internal standard should be added to both standard and Sample solutions. Otherwise it may lead to errors.
* Internal Standard concentration should be same in both sample and standard solutions.
* If Large procedure for sample preparation or extraction procedure is used, Internal standard should be added at the first step itself.
Considerations:
* The internal Standard should be similar to analyte chemically and physically.
* The internal Standard should elute near to main analyte and well resolved.
* The internal Standard should not present in Orginal Sample matrix.
* The internal Standard should be unreactive to sample matrix.
* The internal Standard should be availabel in high pure form
* The concentration of Internal standard should be about to half (either in height or response) to the main analyte. (this is to distinguish two peaks instantly in case of RT shifting).
Thats it..................................
Is this clear to all.......?
Please respond to my article by posting comments to this.......
" Comments are steps to know mistakes.........
mistakes are steps to learn...... "
Thanks
V. Suresh.


Its a nice explanation.... thanks
ReplyDeleteThanx, it is clear expalanation about assay analysis
ReplyDeleteThanks for above explantion but am little bit confused can u clearly explain that method using excell with some examples
ReplyDeleteDear sir please explain about different types of methods for RS in Regular analysis & Validation also
ReplyDeleteEasy to understand.. thx!!
ReplyDeleteNice Explanations Sir. Need Some more guidance Required.
ReplyDeleteTwo components RS calculation by area normalization
ReplyDeleteGood information
ReplyDeleteThank You and that i have a neat give: How Long Renovate House cost to gut renovate a house
ReplyDelete